Common Defects and Analysis in PCB Assembly Shops
PCB Assembly Shops are developing faster and faster, but there are many defects during production.There are many kinds of PCBA Defects such as Tombstoning, cold solder joints, solder bridging, and insufficient wetting, in this artical we will explain their causes, impacts, and prevention/resolution methods. This is a hot topic in quality control.
Tombstoning (Standing Effect) for PCBA Defects and Analysis
Tombstoning refers to the phenomenon where one end of a surface-mount component lifts off the pad, causing the component to stand upright. This defect is very normal in PCB Assembly Shops.
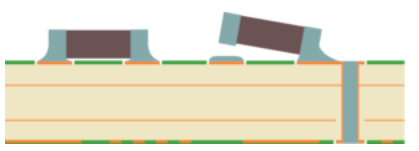
1.Causes
Significant difference in thermal capacity between the two pads of the component: This leads to uneven heating rates, causing the solder to melt at different times.Asymmetric pad design: Results in imbalanced forces on the two ends of the component. Uneven solder paste printing: Creates inconsistent solder volume on the two ends, leading to varying pulling forces during melting.
Excessive reflow soldering temperature ramp rate: Causes uneven temperature changes at the two ends of the component.
2.Prevention/Solutions
Optimize pad design: Ensure symmetry and thermal balance to make the thermal capacity of both ends of the component similar. Achieve uniform solder paste printing: Ensure consistent solder paste volume on both ends by adjusting stencil aperture size and printing parameters. Adjust the reflow soldering temperature profile: Appropriately extend the preheating time to achieve a gentler temperature ramp rate.
Cold Solder Joint for PCB Assembly Shops Defects and Analysis
A cold solder joint appears normal on the surface but lacks a proper metallurgical connection between the component lead and the pad, resulting in unreliable or completely disconnected electrical connectivity. The problem is very serous for quality, so PCB Assembly Shops are paying much attention to that.
1.Causes
Oxidation of pads or component leads: Hinders proper bonding between the solder and metal surface.Insufficient soldering temperature or time: Prevents the solder from fully melting and diffusing.Inadequate flux activity or improper usage: Fails to effectively remove oxides and promote soldering.Moisture absorption in PCBs or components: Affects soldering quality.
2.Impact
Cold solder joints cause unstable electrical connections, potentially leading to intermittent failures and affecting product reliability and lifespan.
3.Prevention/Solutions for PCB Assembly Shops
Strictly control incoming material quality: Ensure pads and leads are clean and free from oxidation.
Optimize the reflow soldering temperature profile: Ensure sufficient preheating and soldering temperature.
Select flux with appropriate activity and control its application volume.
Bake moisture-sensitive materials before use: Enhance post-soldering inspection, such as using X-ray to inspect hidden solder joints.
Solder bridging occurs for PCBA Defects and Analysis
when solder unintentionally connects adjacent pads or pins, causing an electrical short circuit.
1.Causes
Solder paste misprinting or improper stencil aperture design: Leads to excessive solder volume or inaccurate placement.
Component misalignment during placement: Reduces the gap between solder joints, making it easier for solder to bridge.
Improper reflow soldering temperature profile: Causes excessive solder flow.
Solder bridging causes electrical short circuits, leading to abnormal printed circuit boards functionality and potentially damaging components.
Prevention/Solutions
2.Impact
Optimize stencil design: Appropriately reduce aperture size or use trapezoidal openings to control solder volume.
Adjust solder paste printing parameters: Ensure printing accuracy.Improve placement machine precision: Ensure accurate component alignment.Optimize the reflow soldering temperature profile: Properly control solder flow.
Cold Solder Joint (Grainy Appearance) for PCBA Defects and Analysis of PCB Assembly Shops
A cold solder joint exhibits a rough, dull, and grainy surface with low mechanical strength.
1.Causes
Insufficient soldering temperature or time: Prevents the solder from fully melting and forming a proper joint.
Contamination of solder or flux: Affects soldering performance of PCB.
Vibration during the soldering process: Results in an internally loose joint structure.Slow cooling rate: Leads to coarse grain formation in the solder joint.
2.Impact
Cold solder joints have low mechanical strength and are prone to breaking under external force or thermal stress, affecting product reliability.
3.Prevention/Solutions
Ensure soldering temperature and time meet process requirements: Set appropriate parameters based on solder and component characteristics. Use fresh solder and flux: Avoid contamination.
Stabilize the production environment: Minimize equipment vibration.Optimize the cooling rate: Ensure high-quality solder joint crystallization.


